Exocytosis process 746562-Exocytosis process biology
Exocytosis the process of eliminating digested particles out of the cell Endocytosis and exocytosis are two types of active transport, that is, energy is spent during the processes The lysosome is the organelle involved in these processes, as it is responsible for intracellular digestion Exocytosis – The process of transporting molecules out of the cell Phagosomes – Vesicle that is formed around a molecule via the phagocytosis pathway QuizExocytosis is the reverse process, which uses vesicles to release substances to the extracellular space These processes have been suggested to play a critical role in hormone secretion, membrane receptor internalization, pathogen engulfment, and neuronal communications

Exocytosis Process Explanation Proteins Release Mechanism Stock Vector Royalty Free
Exocytosis process biology
Exocytosis process biology-Exocytosis is the process by which cells excrete waste and other large molecules from the cytoplasm to the cell exterior 49 and therefore is the opposite of endocytosis Exocytosis generates vesicles referred to as secretory or transport vesicles ( Chapter 17 ) As compared to endocytosis, exocytosis is a process that is used to transport materials from inside the cell to the external part of the cell by the use of energy Therefore, it is a type of active transport mechanism and it is the opposite of endocytosis Generally, in this mechanism of exocytosis, a special vesicle bound to the cell membrane,



How Do Endocytosis And Exocytosis Maintain Homeostasis Within The Cell Socratic
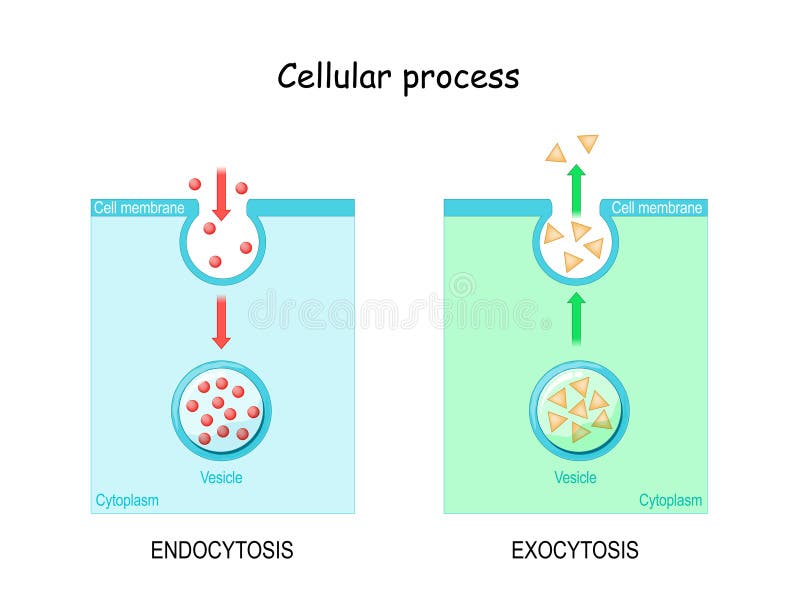
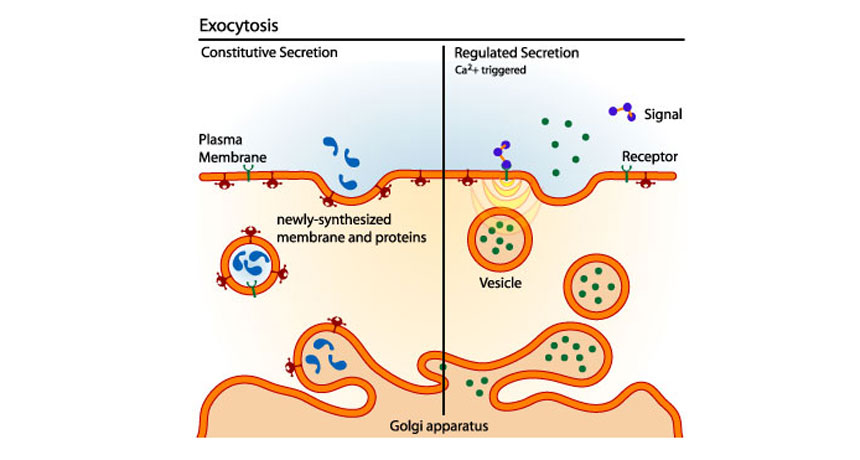
Exocytosis is the cellular process in which intracellular vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with the plasma membrane and release or "secrete" their contents into the extracellular space Exocytosis can be constitutive (occurring all the time) or regulated Constitutive exocytosis is important in transporting proteins like receptors that function in the plasma membrane This is accomplished by the process of exocytosis Opposite to endocytosis, exocytosis involves the formation, transportation, and fusion of internal vesicles with the cell membrane to expel substances from the cellExocytosis This process involves the formation of secretory vesicles that are to be excreted out of the cell Fundamental Types Endocytosis The two primary types of endocytosis are pinocytosis and phagocytosis Exocytosis The two fundamental types of exocytosis are regulated exocytosis and constitutive exocytosis Route of Energy in Transportation
Exocytosis refers to the cellular mechanism, where the transport vesicles incorporate with the cell membrane and eliminate the materials out of the cell via constitutive, regulatory and lysosome mediated secretory pathways Thus, exocytosis merely refers to the process, which expels the biomolecules and metabolic waste from the cell to the extracellular space Exocytosis is the reverse;Soluble and secretory proteins leaving the Golgi apparatus undergo exocytosis The secretion of soluble proteins occurs constitutively In contrast, the exocytosis of secretory proteins is a highly regulated process, in which a ligand must bind to a receptor
Endocytosis is a process that cells use to engulf extracellular material And exocytosis is the opposite process, during which cells expel material into the extracellular space Both endocytosis and exocytosis need energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate or ATP, used in the movement of the substances in and out of the cellGLUT4 is an insulinregulated glucose transporter that is responsible for insulinregulated glucose uptake into fat and muscle cells In the absence of insulin, GLUT4 is mainly found in intracellular vesicles referred to as GLUT4 storage vesicles (GSVs) Here,Exocytosis and endocytosis Active transport and passive transport move ions and smaller hydrophilic molecules across cellular membranes Cells



Endocytosis Stock Illustrations 85 Endocytosis Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Schematics Depicting Fusion And Exocytosis Process Of Insulin Granules Download Scientific Diagram
Exocytosis, as contrast to endocytosis, is a process that uses energy to transfer items from the inside of the cell to the outside of the cell As a result, it is an active transport system that is the polar opposite of endocytosis In this technique of exocytosis, a specific vesicle bound to the cell membrane that contains the cellularExocytosis The reverse process of moving material into a cell is the process of exocytosis Exocytosis is the opposite of the processes discussed in the last section in that its purpose is to expel material from the cell into the extracellular fluid Waste material is enveloped in a membrane and fuses with the interior of the plasma membraneExocytosis is an active process by which substances are moved out of a cell A vesicle or vacuole containing the substance within the cell fuses with the cel
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endocytosis-5ad64d57c0647100386364bb.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples




Exocytosis Active Transport Definition Examples Expii
Below Exocytosis is basically when your vesicles transport materials out of a cell Once the neurotransmitters are synthesised and packaged into vesicles, they are transported until the vesicles reach the cell membrane Then the 2 bilayers rearrange themselves so that the vesicles are able to fuse with the membrane Once that occurs, the neurotransmitters will spill out Exocytosis is a form of active transport that allows cells to move large molecules into the extracellular membrane, where they can be utilized in various ways This is a critical process for all living things, from plants and invertebrates to protozoa and human beings Exocytosis is the process by which cells move materials from within the cell into the extracellular fluid Exocytosis occurs when a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, allowing its contents to be released outside the cell



Scientists Say Exocytosis Science News For Students



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis
Exocytosis is a type of process, in which involves the movement of materials from the inside of a cell to the exterior of the cell by the use of energy Topic Endocytosis Exocytosis Definition The process by which cells actively transport substances into a cell by engulfing them in a vesicle is known as EndocytosisExocytosis Endocytosis It results is expelling molecules outside the cell It helps to ingest molecules towards the cell interior This process leads to the destruction of vesicles This process leads to creation of vesicles There is a discharge of enzymes, hormones, proteins, and glucose Endocytosis is the process of bringing substances inside a cell from the external environment with the help of the cell membrane Through this method, cells acquire nutrients required for growth and reproduction It is a form of the active transport mechanism and thus needs energy, in the form of ATP, to proceed
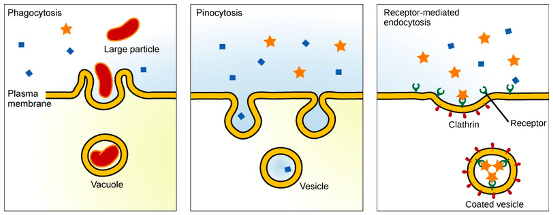



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Transport Teachmephysiology




Exocytosis Active Transport Definition Examples Expii
The process of fusion of a membranous intracellular compartment with the plasma membrane Also refers to the delivery of soluble proteins outside the cell or IMPs to the plasma membrane that results from fusion of a membranous intracellular compartment with the plasma membrane What are the two kinds of exocytosis? Exocytosis is a type of process, in which involves the movement of materials from the inside of a cell to the exterior of the cell by the use of energy Exocytosis is a type of active transport because to perform this process energy is required Exocytosis is the process of expelling oversized particles through the cell membrane To excrete waste and other chemicals, a vesicle forms that surrounds them However, on some occasions, the vesicle is made up of the membrane of the molecule




How Do Endocytosis And Exocytosis Maintain Homeostasis Within The Cell Socratic




Plant Life Endocytosis And Exocytosis
Exocytosis is the process that cells use to release large molecules in vesicles to the extracellular environment Exocytosis is a form of active transport and uses energy Exocytosis Exocytosis means the release of cell products into the extracellular compartment During this process, a vesicle moves from the cytoplasm to the cell membrane, fuses with it, and discharges its content There are 2 general pathways of exocytosis Regulated secretion (stimulusdependent) and Constitutive secretionVideo is an animated explanation of Endocytosis and exocytosisEndocytosis is an energyusing process by which cells absorb molecules (such as proteins) by e




Exocytosis Process Explanation Proteins Release Mechanism Stock Vector Royalty Free




What Is Exocytosis Mbinfo
The process by which substances are released from the cell In this article we will discuss the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis, and we will consider clinical conditions which result from defects in these processesExocytosis is defined as the transport and fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane and the extracellular space There are three exocytosis pathways that deliver vesicles to the plasma membrane Found in all cells, the constitutive secretory pathway operates continuously to deliver freshly synthesized membrane lipids and proteins, and soluble secretory proteins fromVesicle exocytosis releases content to mediate many biological events, including synaptic transmission essential for brain functions Following exocytosis, endocytosis is initiated to retrieve exocytosed vesicles within seconds to minutes Decades of studies in
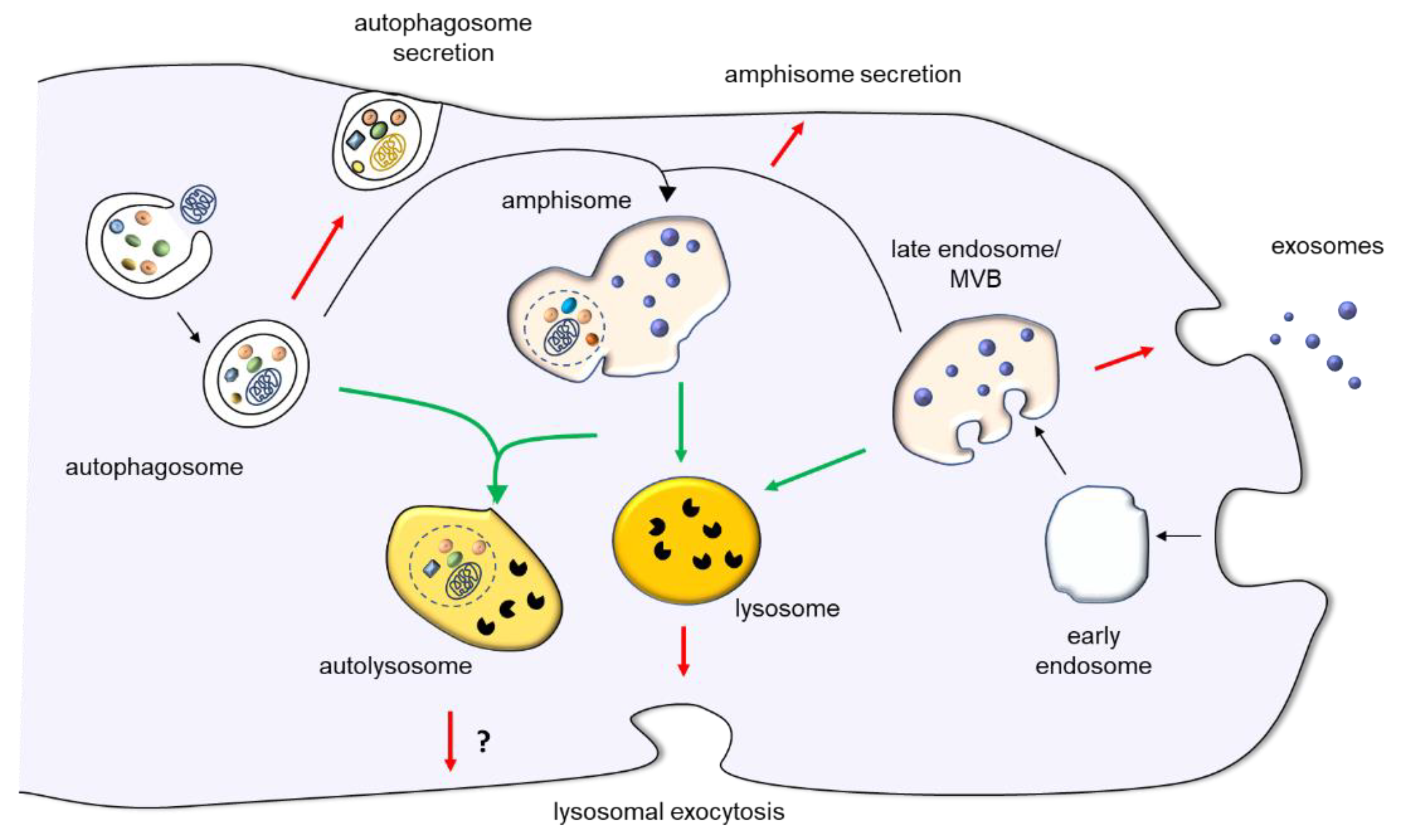



Ijms Free Full Text Lysosomal Exocytosis Exosome Release And Secretory Autophagy The Autophagic And Endo Lysosomal Systems Go Extracellular Html
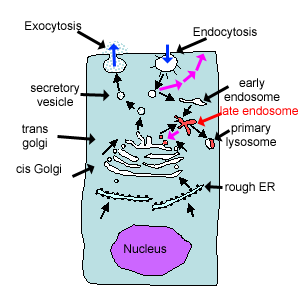



The Cell The Histology Guide
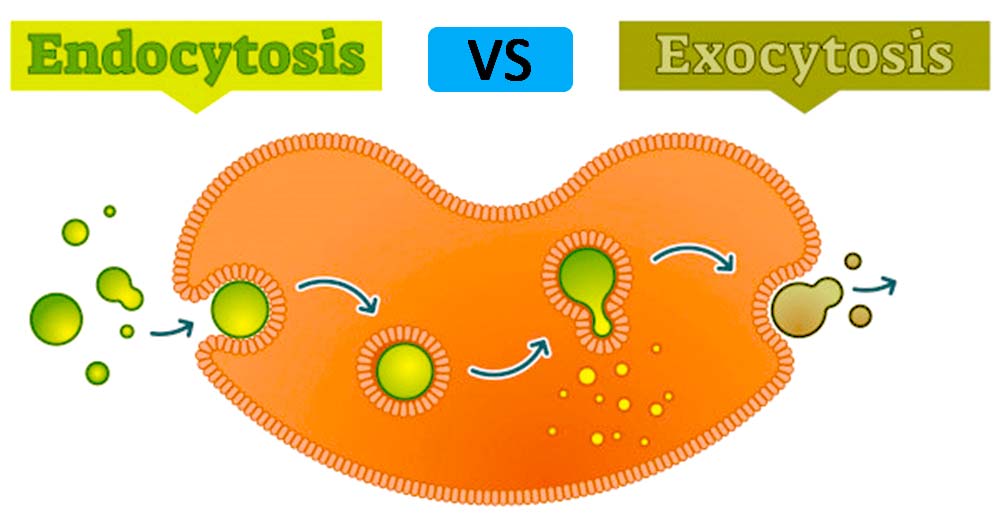
Exocytosis is important in expulsion of waste materials out of the cell and in the secretion of cellular products such as digestive enzymes or hormones Endocytosis, on the other hand, is the process by which materials move into the cell There are three types of endocytosis phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptormediated endocytosis The cell membrane folds in forming a cavity filled with extracellular fluid, dissolved molecules, food particles, foreign matter, pathogens, and/or other substances, a process known as invagination After invagination, the cell membrane folds back to itself until it forms a uniformly enclosed membrane around the trapped molecules and this enclosed membrane or cavity isEndocytosis Definition, 3 Types, Active or Passive?, Vs Exocytosis Definition Endocytosis refers to the process through which materials or particles are internalized into the cell through the invagination of the cell membrane Here, the cell membrane invaginates at the site where the particles to be internalized come in contact with the cell
/exocytosis_2-5ae36dab04d1cf003cef3c48.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples
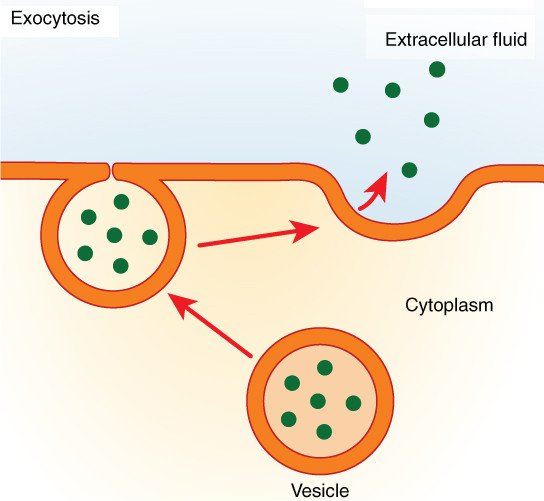



What Is Exocytosis Science Abc
Exocytosis is a process occurring in plant and animal cells that involves moving materials within a cell to the exterior of the cell This process requires energy and is a type of active transport Exocytosis is the opposite of endocytosis in which substances are taken into cells In exocytosis, membranebound vesicles containing cellular Exocytosis, on the other hand, is described as the process of fusing vesicles with the plasma membrane to release their contents to the external environment of the cell The basic difference between Exocytosis And Endocytosis is tabulated below Exocytosis vs Endocytosis Exocytosis Substances leave the cell after being transported through it in vesicles to the Golgi body, where it is then put into secretory vesicles and transported to the cell membrane, where the vesicle fuses with the cell membrane, emptying its contents outside the cell wjec as biology endocytosis exocytosis unit 1




The Cell 5 Vesicular Trafficking Exocytosis Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology




The Exocytosis Endocytosis Cycle Of Synaptic Vesicles At Nerve Download Scientific Diagram
Exocytosis is important in expulsion of waste materials out of the cell and in the secretion of cellular products such as digestive enzymes or hormones Endocytosis, on the other hand, is the process by which materials move into the cellThe secretion of saliva from the pancreas is an example of exocytosis Exocytosis involves the release of material from a cell This happens when secretory cells release their products, for example in the salivary glands and pancreas Substances within the cell are enclosed by a membrane to form what is called a vesicleExocytosis is a process by which cell A) pass substances out of the cell in vesicles B) pass substances out of the cell through the membrane by osmosis C) release substances directly into the extracellular fluid through a pore D) release substances directly into the extracellular fluid through a pit E) identify substances in the environment
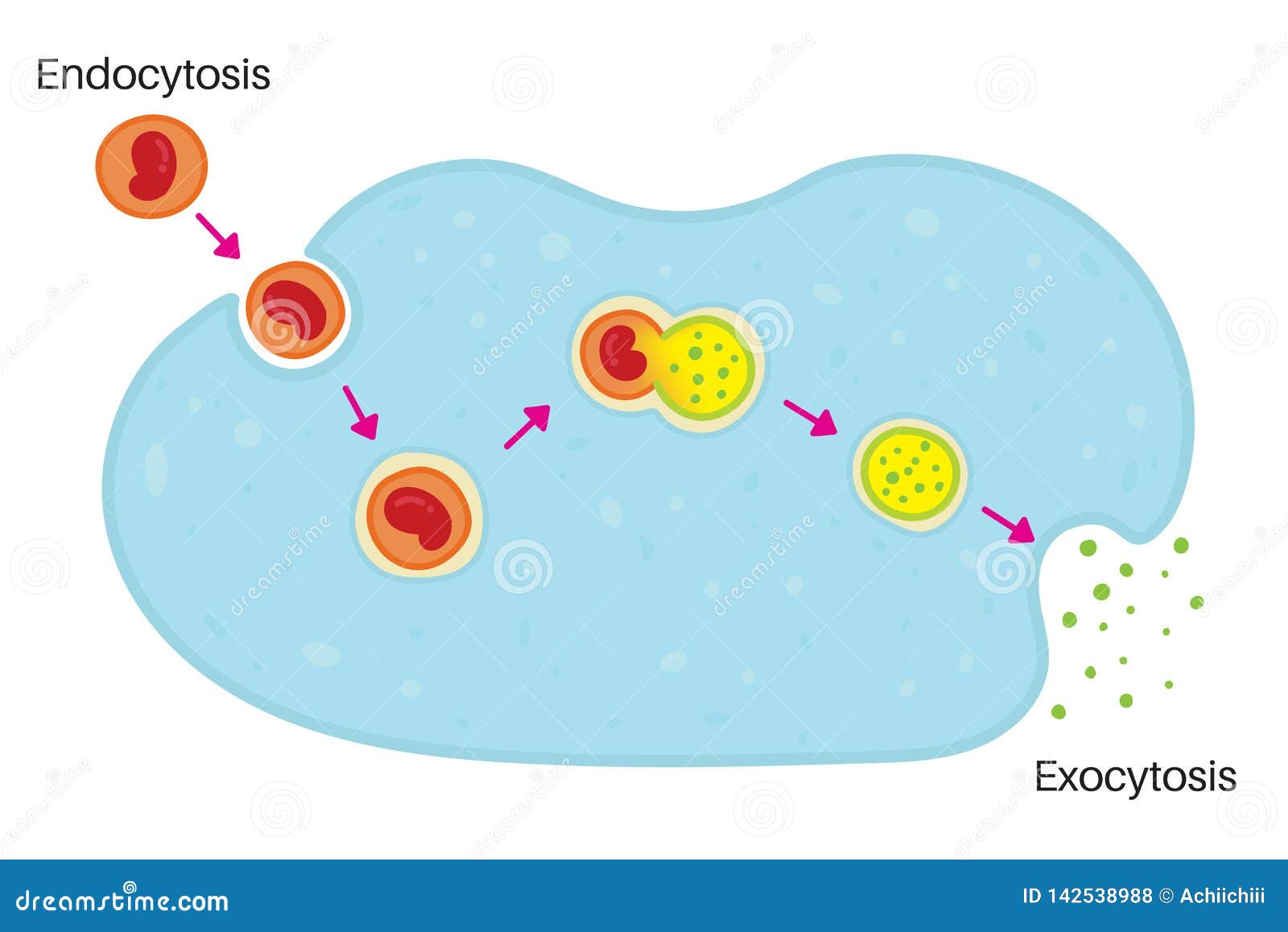



Exocytosis Stock Illustrations Exocytosis Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Endocytosis Exocytosis
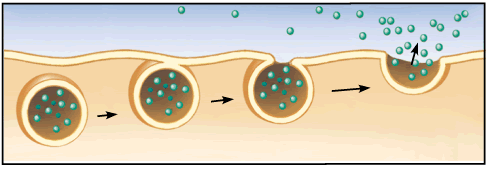
Exocytosis Step 1 Exocytosis Step 2 Exocytosis Step 3 Why would a cell use the process of exocytosis? Basic Process of Exocytosis Vesicles containing molecules are transported from within the cell to the cell membrane The vesicle membrane attaches to the cell membrane Fusion of the vesicle membrane with the cell membrane releases the vesicle contents outside the cell



1




3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Key




Exocytosis Endocytosis Receptor Mediated Endocytosis Ppt Download




Exocytosis Examples Triggers What Is Exocytosis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks




Exocytosis Process Primary Active Transport Across Cell Editorial Stock Photo Stock Image Shutterstock




Endocytosis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Learn About Diagram Of Exocytosis Chegg Com




Endocytosis And Exocytosis The Science Notes




Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Difference Between Exocytosis And Endocytosis Difference Between




Exocytosis Biology Britannica




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Plasma Membrane Mcat Content




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I




3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Ppt Download




Exocytosis Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



17 4 Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology Libretexts




Measuring Ca 2 Dependent Lysosomal Exocytosis A Lysosomal Exocytosis Download Scientific Diagram




Hillis2e Ch05




Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis




Steps In Neuronal Exocytosis Synaptic Vesicles Containing Download Scientific Diagram
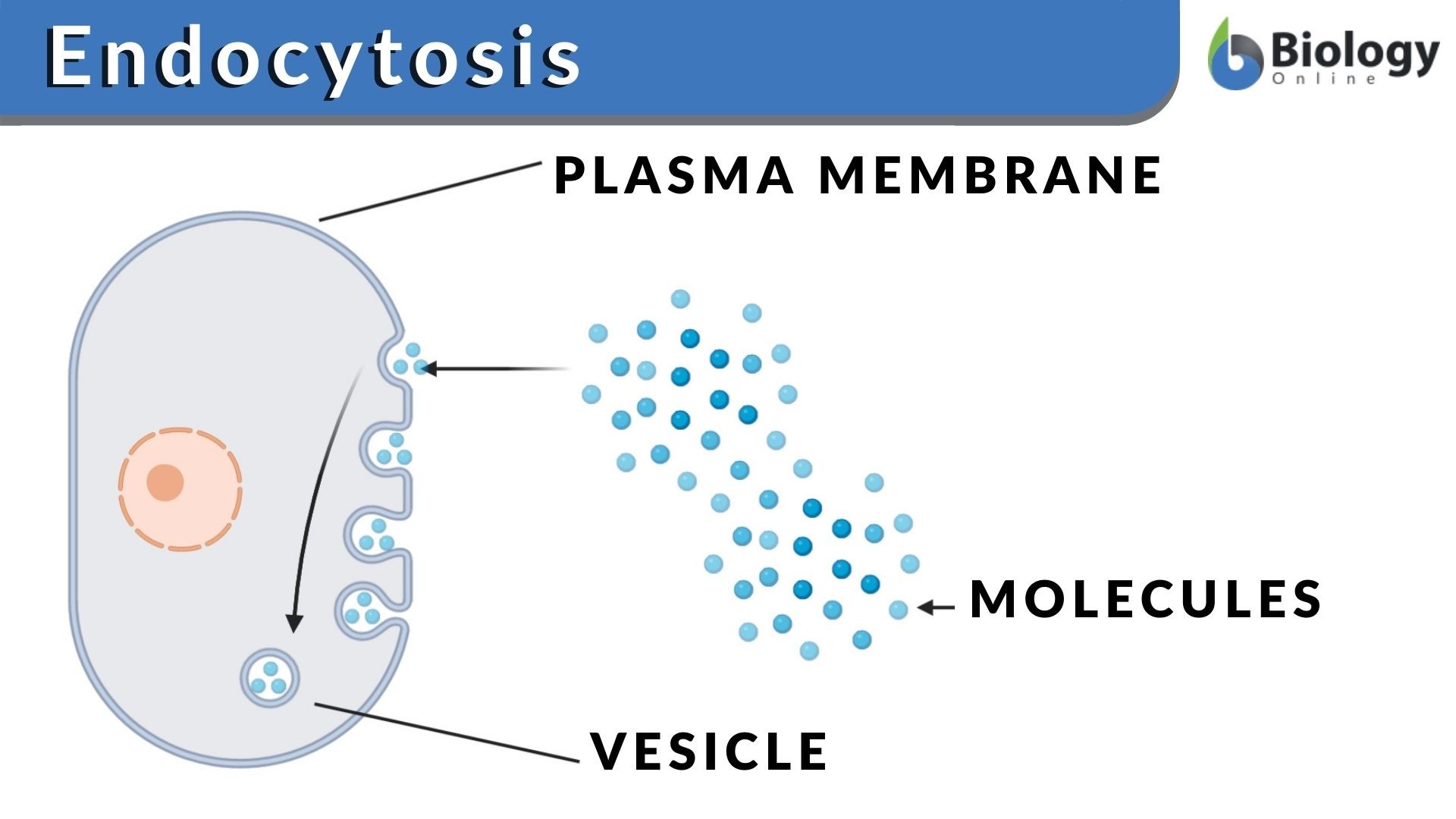



Endocytosis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
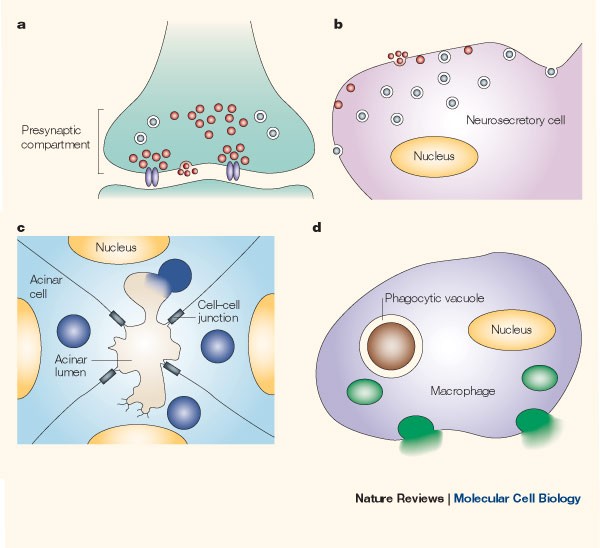



Regulated Exocytosis New Organelles For Non Secretory Purposes Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology




The Cell 5 Vesicular Trafficking Exocytosis Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology




Exocytosis Wikipedia




Actin Remodeling In Regulated Exocytosis Toward A Mesoscopic View Trends In Cell Biology




File Exocytosis Types Svg Wikimedia Commons




Exocytosis Video Membrane Transport Khan Academy




3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Key
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_process-5ae370b4a9d4f900373c9b48.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples
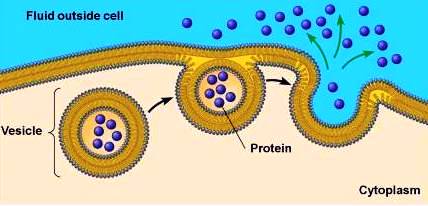



What Is The Relationship Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Socratic




Active Transport The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




Stages Of Exocytosis In Secretory Cells A Formation Of Vesicles B Download Scientific Diagram




The Cell Membrane Passive And Active Transport The Biology Primer
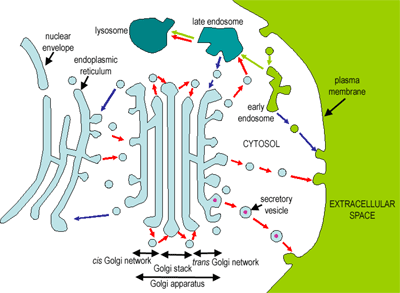



The Cell The Histology Guide



Compare And Contrast Endocytosis And Excocytosis Enotes Com




Schematic Diagram Of Polarized Exocytosis Process The First Stage The Download Scientific Diagram
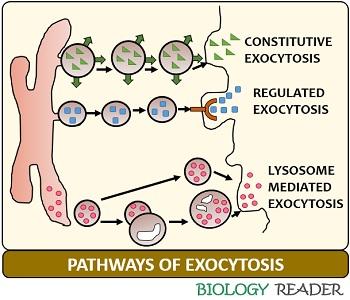



What Is Exocytosis Definition Pathways Steps Example Biology Reader




Ucx9k4clgftdim
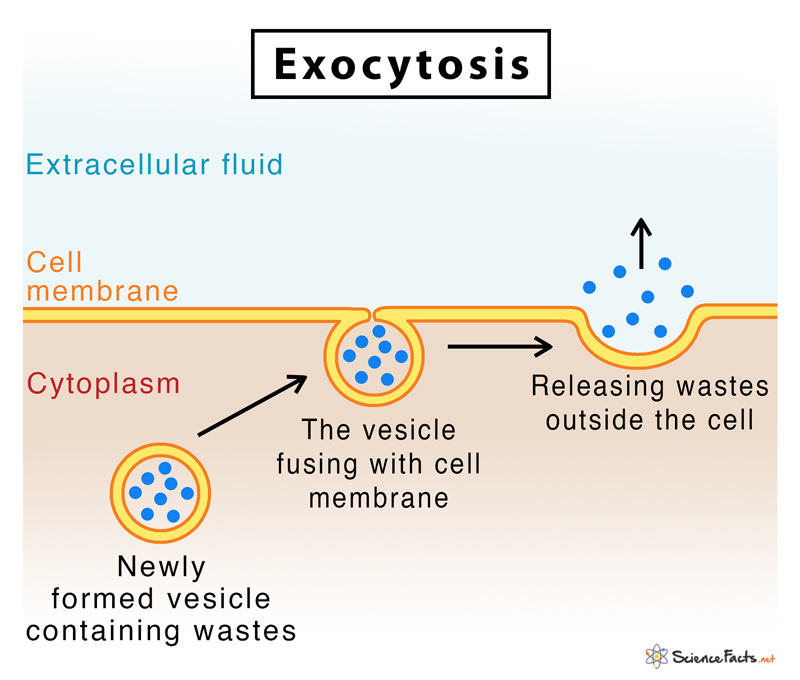



Exocytosis Definition Functions With Examples Diagram




Phagocytosis Neutrophil That Uses Its Plasma Membrane To Engulf A Bacterium From Endocytosis To Exocytosis Educational Scheme Digestion Process In Phagocyte Immune System Mechanism Vector Illustration Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock
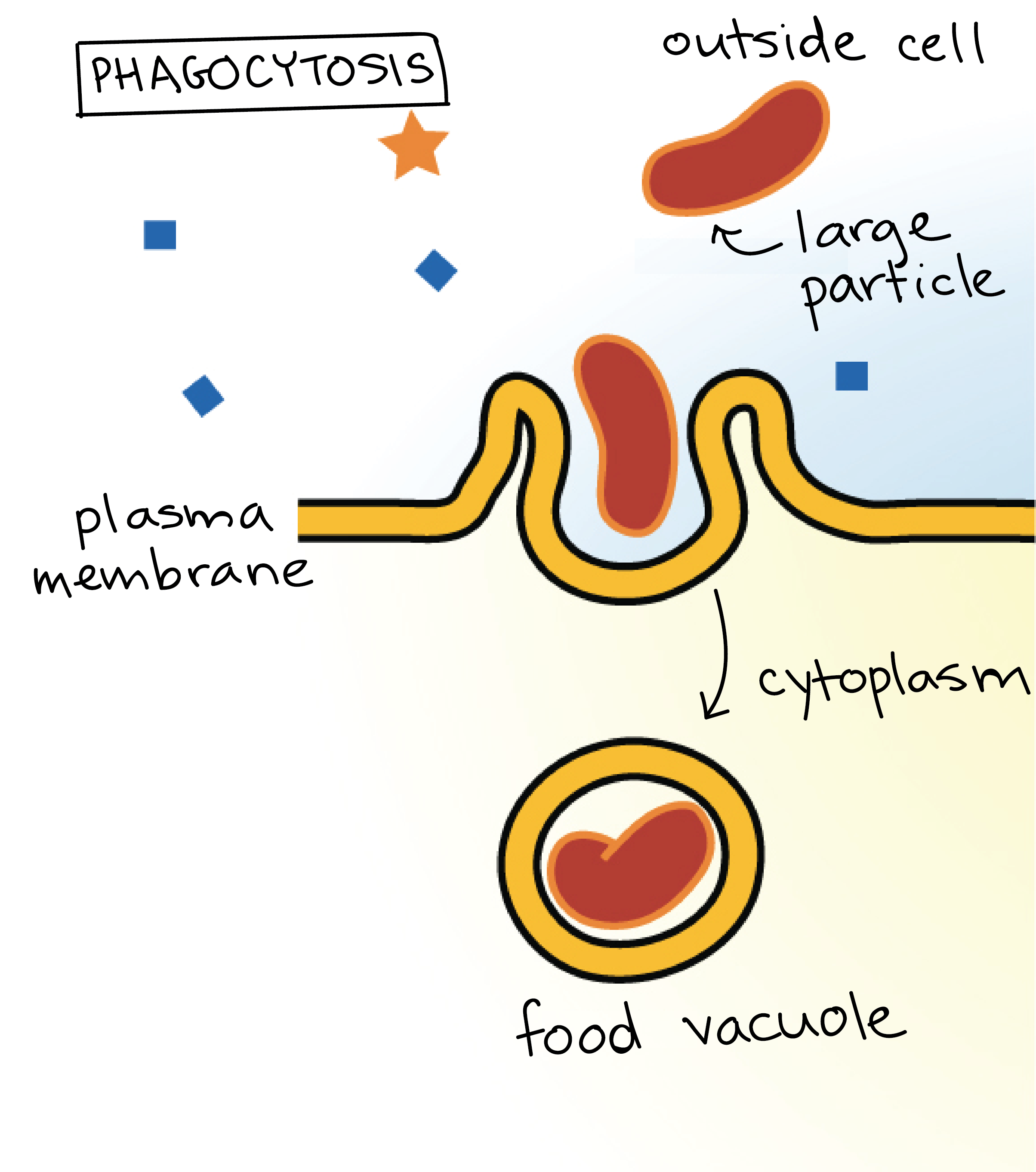



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy




Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




The Exocytosis Process Exocytosis Consists In Secretory Vesicle Download Scientific Diagram




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I
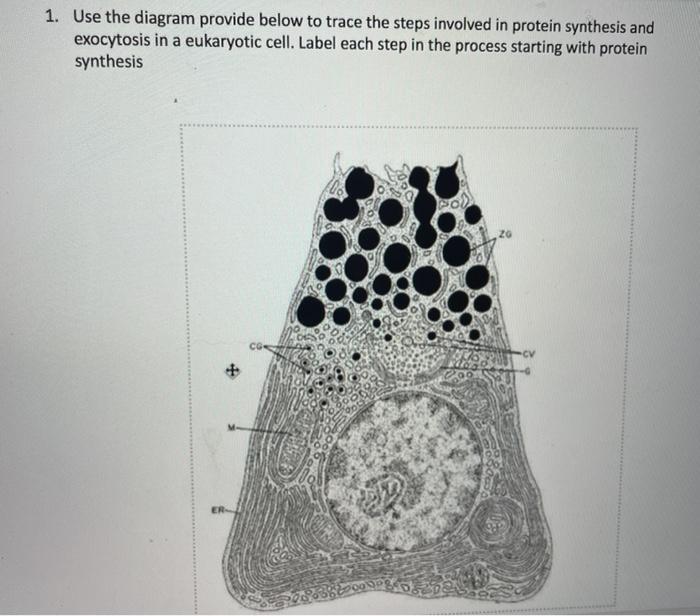



Solved 1 Use The Diagram Provide Below To Trace The Steps Chegg Com




What Process Is Shown A Endocytosis B Phagocytosis C Pinocytosis D Exocytosis Brainly Com



2 17 Exocytosis And Endocytosis Biology Libretexts



1




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Plasma Membrane Mcat Content




Exocytosis Easy Science Easy Science Body Systems Flashcards



Exocytosis Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Function Process System Blood Membrane Molecules




Exocytosis Examples Triggers What Is Exocytosis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Exocytosis
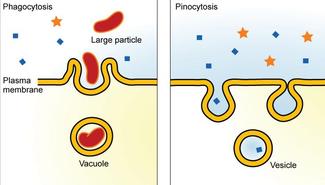



Cells Endocytosis Exocytosis Pathwayz



Endo And Exocytosis Book Chapter Iopscience




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks
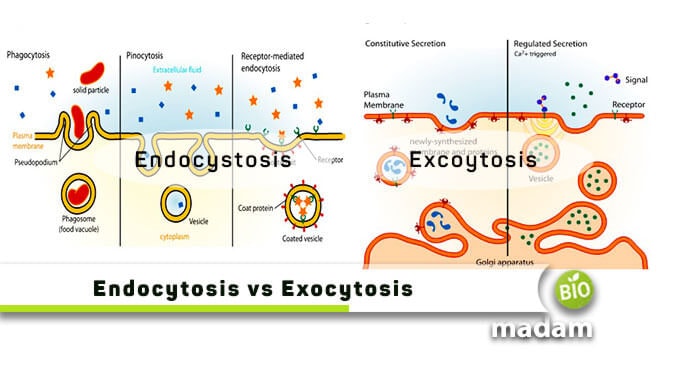



Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biomadam




Ppt Endocytosis Exocytosis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
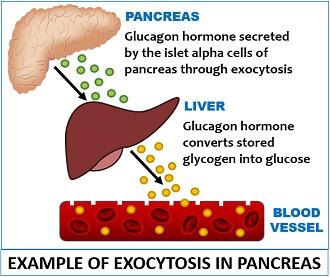
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/glucagon_glycogen_glucose-5ae36ebc8023b90036236782.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples
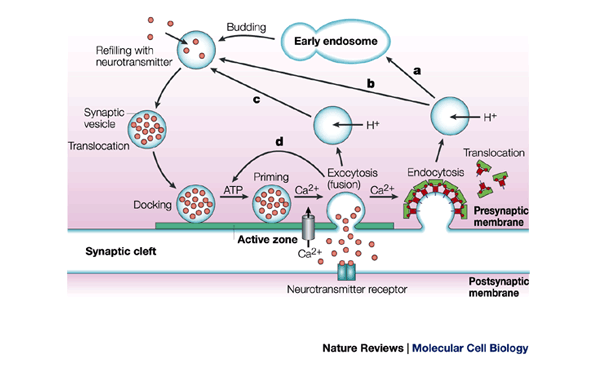



Temporal And Spatial Coordination Of Exocytosis And Endocytosis Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology




Exocytosis Wikipedia




Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Which Process Is Shown In The Image A Active Transport B Endocytosis C Exocytosis D Passive Brainly Com



Vcac Cellular Processes Constitutive Secretion Golgi Advanced Look Exocytosis




Exocytosis A Process For Primary Active Transport Across The Cell News Photo Getty Images




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation



Biodotedu



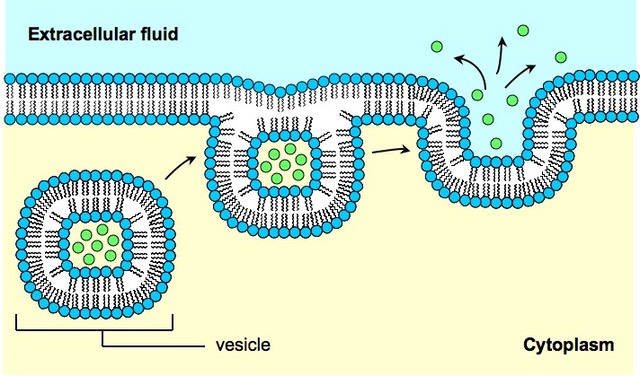
What Is Exocytosis Definition Pathways Steps Example Biology Reader



Bulk Transport Bioninja




Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
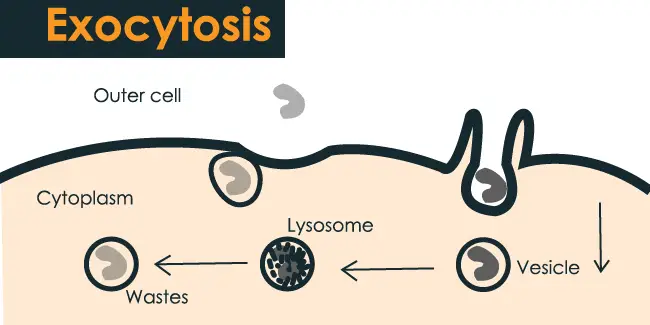



Exocytosis Definition Types Steps And Examples 6 27




Exocytosis A Process For Primary Active Transport Across The Cell Membrane Stock Photo Alamy




5 4b Exocytosis Biology Libretexts
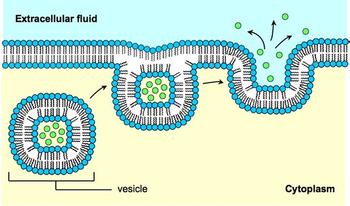



Cells Endocytosis Exocytosis Pathwayz
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis-582df6965f9b58d5b183203f.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples




Chapter 3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Outside Inside Sketch Molecules Entering A Cell By Active Active Transport Trans Ort 1 Outside Endocytosis Exocytosis Pdf Document




What Is Exocytosis Explain With The Help Of Diagram Brainly In




Exocytosis Biology Britannica



1
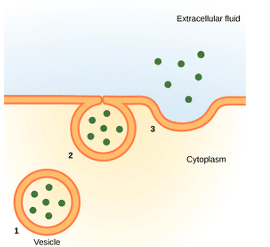



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Transport Teachmephysiology



Endocytosis Diagram
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/golgi_exocytosis-5ae36c743de4230037581736.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples
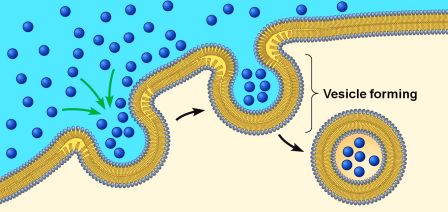



What Is The Relationship Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Socratic
コメント
コメントを投稿